

It will explain good 3/4 of reactivity in the course, so it’s an extremely important topic to master. Resonance in chemistry is a tool used (predominately in organic chemistry) to represent certain types of molecular structures. Unfortunately, this detail has been lost in the. Resonance is one of the most important topic in organic chemistry bonding. These formal bonds are needed to define the wave functions of a complete set they connect electrons with opposite spin in a carefully defined way. When Linus Pauling developed resonance theory, he defined resonance as the superposition of wave functions.
While all the examples above are, strictly speaking, conjugated, we’ll only be referring to the multiple π-bonds participating in resonance as “conjugated system” due to their special chemical properties. We’ll be talking about those interactions in a lot of details when we discuss the conjugated system. Two (or more) π-bonds interacting with each other.

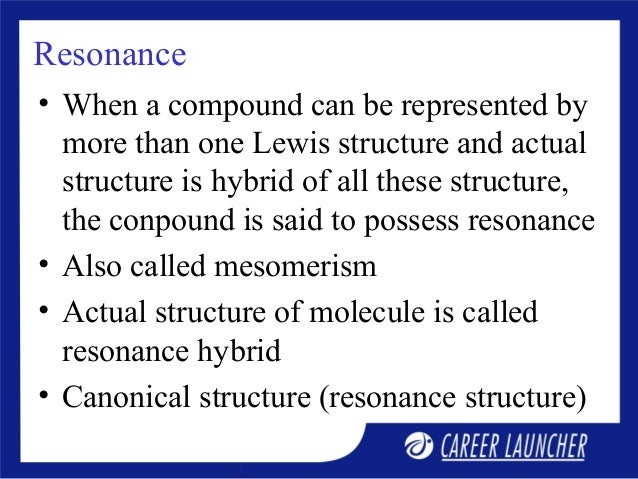
However, those are very important for certain types of reactivity, particularly, acid-base chemistry. We’re not going to focus as much on the anions in organic chemistry as on cations. A molecule or ion with such delocalized electrons is represented by several contributing structures (also called resonance structures or canonical forms). An electron pair and an adjacent π-bond produce allylic or benzylic anions. Resonance is a way of describing delocalized electrons within certain molecules or polyatomic ions where the bonding cannot be expressed by a single Lewis formula. Those would be examples of allylic and benzylic systems. Resonance Kota: Best Coaching Institute for IIT-JEE, JEE Main (AIEEE), JEE Advanced and Pre-Medical (AIPMT, NEET, AIIMS), Commerce & Law across India. An interaction between the empty orbital and a π-bond. That generally results in a structure analogous to a simple π-bond. An interaction of an empty p-orbital and an adjacent electron pair. There are 4 types of resonance that you’ll have to know within the scope of your organic chemistry course. However, there are situations when three or more orbitals can interact making a much longer and much more complex orbital interaction system. A case of a simple π-bond results from the interaction of the two p-orbitals connecting two atoms. A molecule or ion with such delocalized electrons is represented by several contributing structures2(also called resonance structuresor canonical forms). By resonance in organic chemistry we mean an interaction of multiple p-orbitals making a long π-bond spanning multiple atoms. In chemistry, resonanceor mesomerism1is a way of describing delocalized electronswithin certain moleculesor polyatomic ionswhere the bonding cannot be expressed by one single Lewis formula.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
